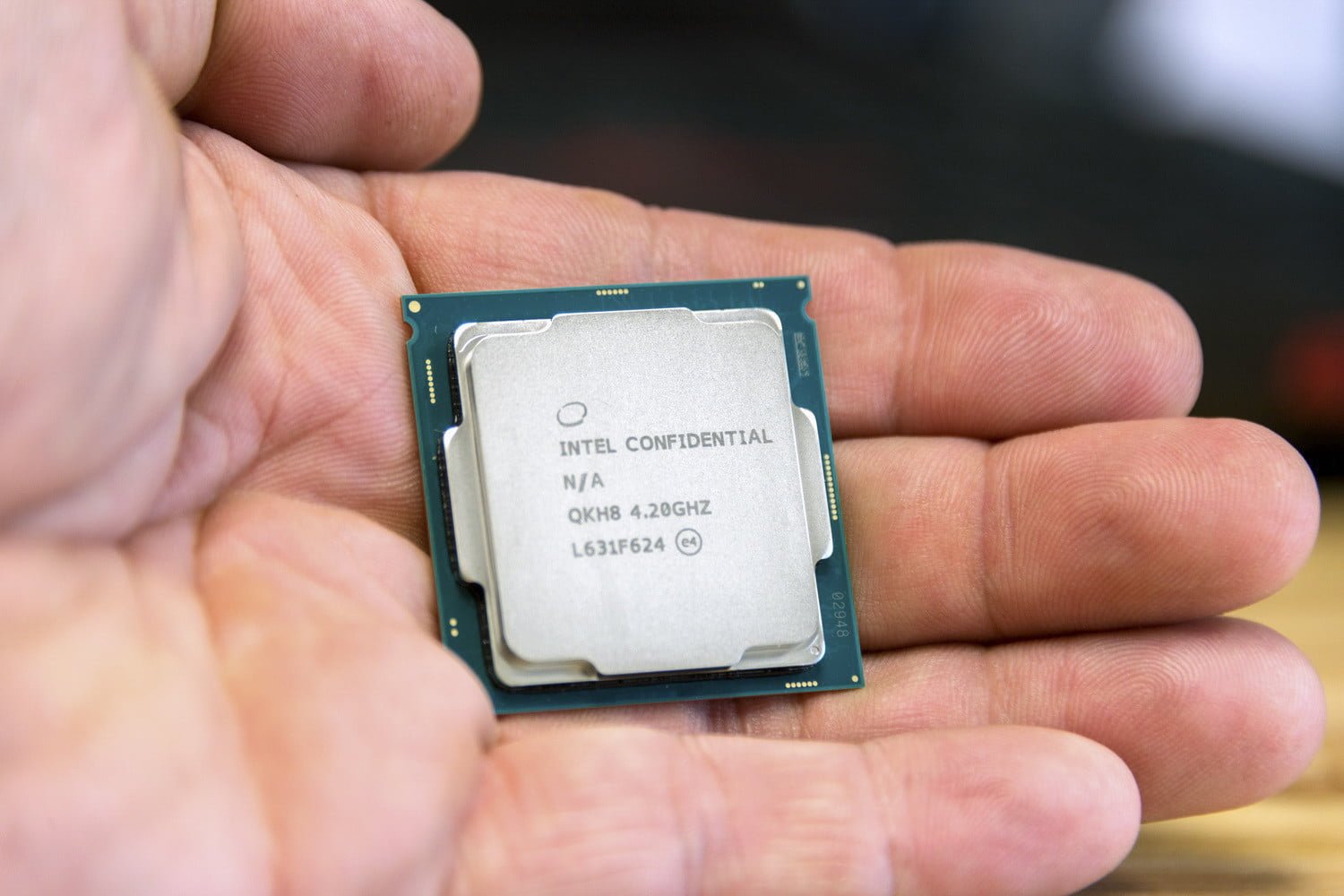

The processor is one of the most important components for running your gaming PC. It is also known as the CPU or central processing unit. It is responsible for providing instructions and the processing power your PC needs to do its work.
When buying a processor, you must consider buying a powerful processor. The newer your processor is, the more it can help your gaming PC run and work faster.
Identifying the model of your unit’s processor is also important, especially when installing a new game that requires a specific processor model. Below is a guide on identifying the model of your Intel processor and the specifications you need to check before buying one.
How to Identify the Intel Model
You can identify the model of an Intel processor by checking the following:
- Operating System
- Packaging Box
- Processor Unit
Check the guide below for each:
1 – Operating System
For Windows Operating System
- Step 1 – Click on the Windows icon in the taskbar, and click on the Gear Icon. Select System and scroll down to the bottom until you see “About.”
- Step 2 – Choose About, and you see your PC’s Processor information. It should include the model’s name, number, and processor speed.
To identify which is the model name, the number, and the processor speed, you can refer to the details below:
- Model Name: Intel Core i5
- Number: i5-5300U
- Processor Speed: 2.30 GHz
- You can also access the Processor information via your keyboard. Press on the Windows key and type “System,” then click Enter.
- Choose System Information. This will show the details about your processor unit. Aside from the brand name, number, and speed, it will also show the cores and the number of processors. Refer to the details below to identify which of which:
- Model Name: Intel Core i5
- Number: i5-5300U
- Processor Speed: 2.30 GHz
- No. of Cores: 2
- No. of Processors: 4
For Linux Operating System
- Step 1 – Open the command window in your Linux system by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T keys simultaneously.
- Step 2 – Type the following command:
lscpu | grep “Model name”
You can refer to the screenshot below:

For MAC OS
- Step 1 – Instead of a command window, Mac OS uses the Terminal app to enter commands on the system. To access the Terminal app, click the Launchpad icon in the Dock.
- Step 2 – Type “Terminal” in the search field and click its icon.
- Step 3 – Type the following command in the terminal app to see your processor information:
sysctl -a | grep machdep.cpu.brand_string
Check for the reference below:

2 – Packaging Box
You can also identify the processor information on the model’s packaging box. Of course, you need to make sure you’re buying an authentic OEM unit with an Intel Boxed Processor.
The packaging box has the model’s information, including the number of the processor. It also includes several details, including the batch number (FPO) and the serial number (ATPO).
Check for the reference below:

3 – On the Processor Unit
Another way to identify the model of your processor is by checking the unit itself. You can find the name and the number of the Intel Processor on the top of the model.
Check the reference below:
What are the Specifications You Should Look for in a Processor
Another part of checking your processor is to check its specifications. Below are the different features you should look for in a processor:
- Base Clock Speed
The clock speed refers to the number of cycles it can perform every second. The higher the clock speed your unit has, the more tasks it can handle and process. This will make your gaming PC run faster.
- Max Turbo Speed
Intel processors can operate above their typical frequencies when needed. This technology is called Turbo Boost, which increases the clock speed and allows your processor to run even faster.
- Overclocking
Overclocking is a feature that can increase the base clock speed of your processor. Not all Intel models can be overclocked; only models that end with a “K” or “X” can be overclocked.
However, suppose you’re planning to overclock your processor. In that case, your PC build needs an excellent cooling system as an overclocked CPU can generate more heat.
- Core Count
The current processors have multiple cores. The more cores your processor has, the faster it can handle multiple processes in your system. This is very important for multi-tasking or if you’re running programs with heavy workloads.
- Multi-Threading
The number of threads on your processor refers to the number of virtual cores the unit can simulate. Intel processors use “hyper-threading” technology to achieve this simulation. And the more threads your processor has, the better your PC can run on multitasking.
- L Cache
The L caches of your Intel processors increase with each level (L1, L2, and L3). As the cache capacity of the processor increases, the more it takes longer for a processor to search for the needed data.
- Integrated Graphics
Integrated graphics on your processor can be very helpful when troubleshooting discrete graphics. It also helps display the image or graphics on your monitor even if the GPU is malfunctioning.
Intel uses HD Graphics, UHD Graphics, and Iris.
***
For more tips and how-tos on gaming PC builds, follow our blog.
Source: